Key Takeaways
- Title tags are a HTML code snippet that helps users and search engines understand what your webpages are about
- A good title tag is 50-60 characters long and tells the reader about the central topic of a webpage at a glance
- Title tags should be optimised based on keyword research, user search intent and your SEO strategy
- Writing and optimising title tags is an ongoing process that should be part of your regular SEO efforts
What are title tags?
A title tag is a piece of HTML that’s used to define the title of a webpage. Title tags aren’t displayed on-page, but they are displayed in search engine results, browser tabs and social media posts.
Title tags are read by both users and search engines. The ideal title tag should:
- Outline what the page is about
- Be descriptive yet brief
- Incorporate keywords that match your SEO strategy and the content on the page
- Be understandable by website visitors and search engines
This helps search engines correctly categorise the page, and it helps users confirm that the page is relevant to their search.
Title tags play an important role in SEO. They’re used by search engines to “crawl” your page and make sense of the content. They are also the user’s first impression of a webpage. This can make or break their interest in your brand, so it’s important to get it right!
How are they different from H1 tags?
A title tag is not the same as a heading tag. Both are HTML-based, but they’re used differently. These two types of tags are often confused because it’s common for them to use the same (or similar) copy.
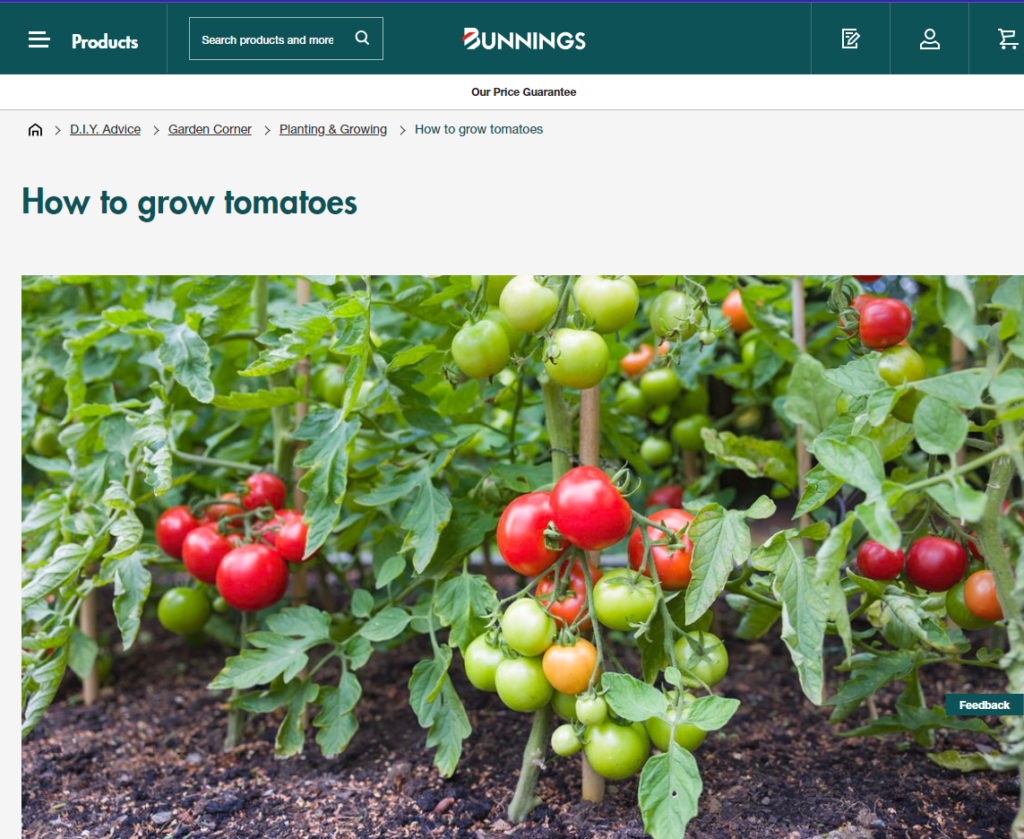
Here’s an example of a H1 tag on the Bunnings website. This is what the HTML looks like:
<h1>How to grow tomatoes</h1>
This is what it looks like on the page:
Compare this to the Title Tag from the same page:
<title>How To Grow Tomatoes</title>
This is how it’s displayed in Google’s search results:

In the two images above, the copy “How to grow tomatoes” has been used as the page title and the heading tag. You might still be scratching your head saying, “But they look the same?” So, here is a brief recap of the two and how they differ:
- Page Title Tags – Are an HTML element used to define the page title. This is displayed as the clickable headline in search results.
- Heading Tags – Are an HTML element used to define headings for a page, paragraph or section. They rank in order of importance from H1 to H6.
The impact of title tags on search engines
The titles given to your web pages are indexed by search engines. They’re one of the ways that your content and website is matched to user search queries.
A good title tag can help your website rank higher in the search results – they’re so important that they can be the difference between position #1 and #2. The more relevant your title tag is to the search query, the content on the page and your keyword strategy, the higher the page will rank.
What is the ideal title tag length?
The ideal title tag is 50-60 characters long. Title tags that are over 60 characters will be cut off, which is bad for SEO and user experience. The character limit is based on the number of pixels needed to display the title in Google’s search results.
Should a title tag include your brand name?
Since the character count is limited, it can be difficult to tell whether or not to include your brand name in title tags.
Including your brand name is a good way to build brand awareness and leverage existing brand equity. But it also eats into your character count, which might require you to compromise on keywords and accurate descriptions of the page content.
The big question to ask yourself is, “How much brand equity does my company have?”
If you have lots of equity, including your brand name can be a great way to attract visitors to your website. If you have low brand equity, you may be better off focusing on keywords that align to your customers’ search queries.
But brand equity isn’t the only factor to consider.
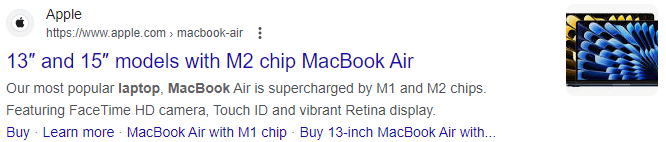
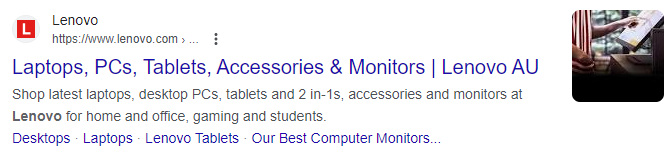
For instance, Apple is so recognisable that they don’t even need to display their brand in title tags. On the other hand, Lenovo displays theirs because it helps distinguish their Australian site from other regions. That’s important for improving user experience and serving up web pages that match user search intent.
There’s no right or wrong answer when it comes to using your brand name in title tags.
For most companies, we recommend writing a first draft of your title tag without your branding. Accurately describe the content on the page and include your core keywords. If you have enough characters remaining, including your brand name is a great way to build awareness.
What does the HTML code look like?
The HTML code of a title tag looks like this:
<title>Example Title Tag</title>
The code should be placed in the section of the page’s HTML. If you are using a Content Management System (CMS) such as WordPress, you can edit title tags from the website dashboard without writing code. If you aren’t using a CMS, title tag HTML appears like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML Elements Reference</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
How title tags appear in SERP, Browsers and Social Media
Having clear and relevant page titles improves user experience and can result in an increased click-through rate from the Search Engine Results Page (SERP). Think of your page title as a headline that encourages people to click on your result.
Here’s how page titles are displayed on Google’s SERP:
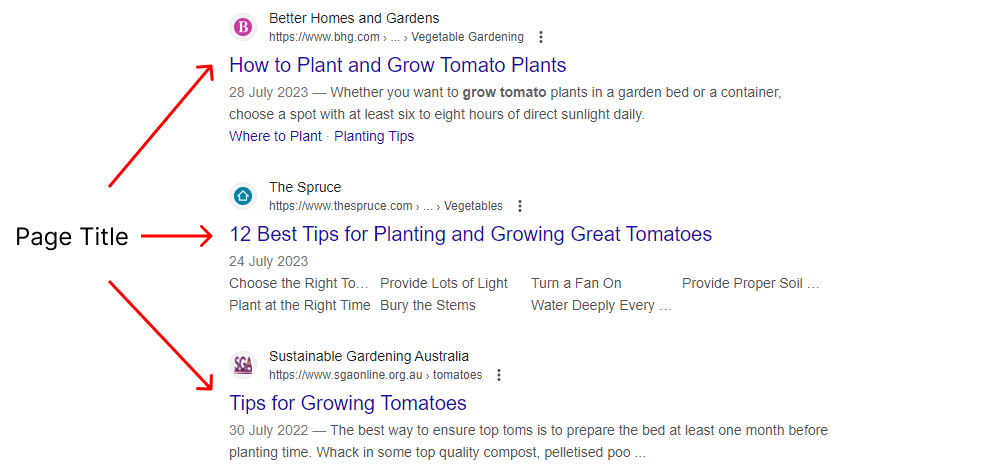
Page titles are also displayed by your web browser. Each browser displays page titles a little differently, but it’s common for the title tag to show up in tabs like the example below. This helps users select the correct page when they have multiple tabs on the go:
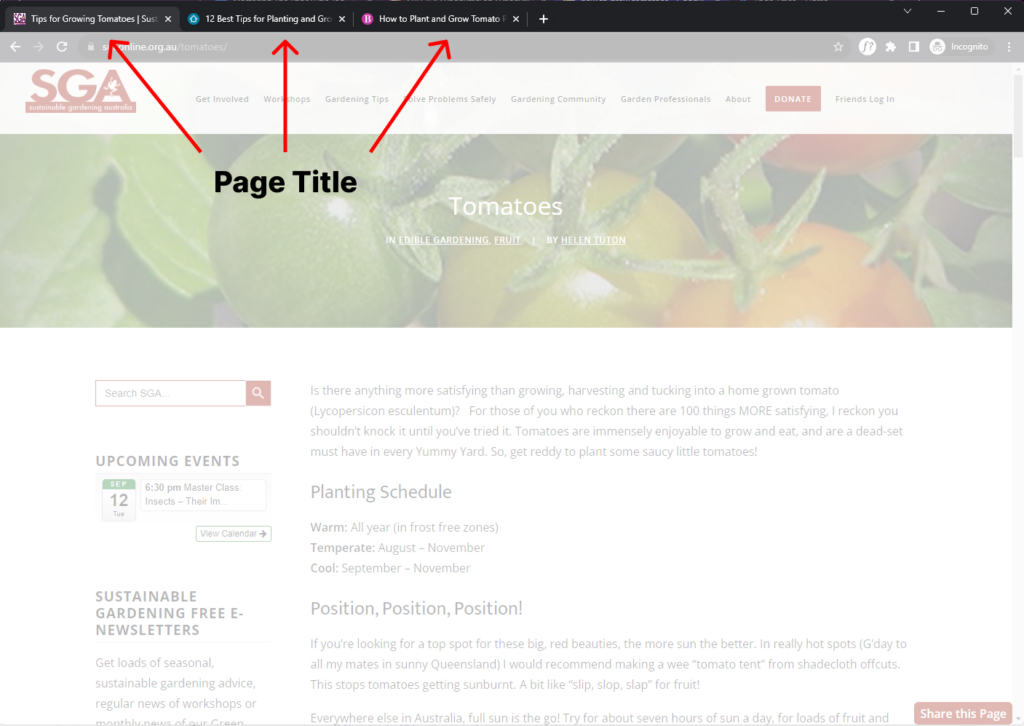
Finally, title tags are also displayed when posting links on social media platforms. Each social platform displays title tags in a similar way. It’s common for social posts to display the page title, feature image and meta description. This helps users understand where they’ll be taken if they click on a link:
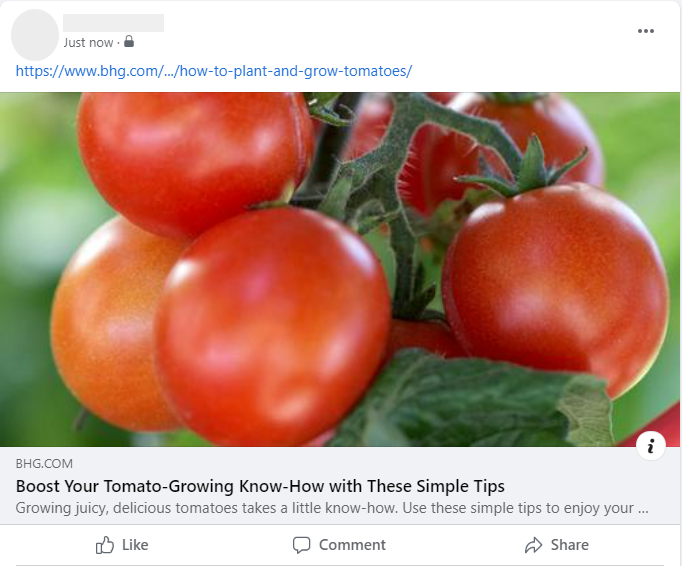
Feature images and meta descriptions are often overlooked when building a website. Failing to include images and meta descriptions is a missed opportunity to provide additional information to users and search engines!
How to write a good title tag for SEO
Writing a good title tag for SEO takes time, practice and patience. With the complexity of search engine algorithms, there are a few ways to approach writing title tags, but there’s also an element of trial and error.
Search results are based on hundreds (if not thousands) of variables. That means you’ll need to periodically tweak page titles to ensure they’re always performing at their best.
It all starts with keyword research!
Ah yes, keyword research. It’s the foundation of SEO, and it has a huge impact on title tags.
Title tags have a very limited length. Since we don’t have much room for keywords, it’s best to select a primary keyword that aligns with your SEO strategy for that particular webpage.
Once you have chosen your primary keyword, place it as close to the beginning of the title tag as possible. You should aim to be grammatically correct – avoiding stuffing keywords into a title tag if they won’t make sense when read by a human.
You can add modifiers to your primary keyword to create long-tail variations. For example, the content on a webpage might be targeting multiple key phrases. We can use these phrases to modify the primary keyword when writing the title tag:
- Primary Keyword: “how to grow tomatoes”
- First long-tail keyword: “how to grow tomatoes in Queensland”
- Second long-tail keyword: “how to grow tomatoes in pots”
- Title tag: “How to Grow Tomatoes in Pots in Queensland”
This can also be useful if you want to rank multiple pages that use similar primary keywords, but want to avoid cannibalisation by search engines.
Title tag best practice
Writing title tags is equal parts art and science. You will probably need to test a variety of title tags until you find one that’s perfect for your content.
In the meantime, you can give your title tag a better chance of success by following these best-practice rules:
- Stick to the 60-character limit (including spaces)
- Write for humans, not search engines
- Use one primary keyword
- Avoid keyword stuffing
- Make titles unique
- Make titles relevant to the page content and search intent
- Use correct capitalisation
- Accurately describe the page’s content or purpose
It’s common for title tags to use “action” words. Action words get the reader excited and can encourage them to click on your page. Examples of action words include:
- Detailed
- Essential
- Easy
- Fast
- Best
- Top
- Proven
You can also use numbers as part of a title tag. You know the ones – “Top 5 Tips For Writing SEO Title Tags” or “Lose Weight in 10 Easy Steps”.
Using numbers can help quantify what a user will find on your website, which may encourage them to click your link before trying other results.
Common mistakes – title tag tragedies
Page titles have a huge impact on the SEO value of your website and how visitors interact with your content.
Users only click on links they believe will be relevant to their search query. Therefore, you need to avoid common mistakes that lead to title tag tragedies:
1. Missing Titles
<p>
The most obvious mistake is not having a title tag in the first place! If you haven’t included a page title in your HTML, you run the risk of a search engine making up a page title for you (more on that later).
You can quickly check what page titles your website does or doesn’t have using tools like:
2. Overly Long Titles
A common mistake is overly long title tags. This leads to page titles being truncated, and users may miss out on important information or keywords that were supposed to appear in the title.
Below, we’ve provided an example of the correct length and use of a title tag, as well as a good use of the page’s meta description:
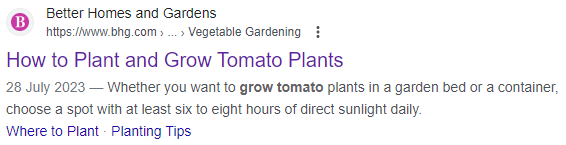
But, when title tags get too long, they aren’t displayed properly. This leads to the title (and the meta description in this case) being cut off:
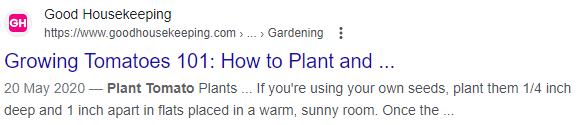
In this example, losing part of the title tag makes it much harder for users to figure out what the page is about. That can make all the difference when it comes to attracting organic traffic from search engines!
3. Duplicate or Similar Titles
Using the same page title for multiple pages is bad for SEO and user experience. This often occurs when a new page is created by duplicating an existing page without changing the metadata. Each page needs a unique title tag and meta description to help search engines and users understand what the content is about.
Duplicate title tags make it hard for Google to determine which page matches the user’s search query. When this happens, Google often won’t display any of your pages.
The other risk is that website visitors leave your page right away because it doesn’t match their search query. This causes a high bounce rate, which indicates a poor user experience.
4. Keyword Cramming
Using the same keyword multiple times (or variations of the same keyword) will not improve your chances of ranking for particular search terms. Keyword cramming is confusing to users and search engines.
For example, the title tag we’ve used here includes a single keyword:

Using one keyword helps search engines understand what our website is about. It also means potential visitors can see what the website is about at a glance.
We could cram a bunch of keywords in there with a title like “SEO Agency Brisbane | Brisbane SEO Agency | SEO Experts” but that would create confusion. The title repeats itself so many times that it’s difficult to read. That’s bad for user experience, and user experience is the most important factor when writing title tags.
5. Incorrect Use of Capitalisation
It’s common to use capitalisation as a way to make your webpage stand out in search results. Doing this incorrectly can make your links appear spammy, which can scare away potential visitors. The common forms of title tag capitalisation are:
- Title Case – Where the main words of the title have a capital letter, but smaller words such as ‘and’ are lowercase
- Sentence Case – The first letter of the first word is uppercase, and the rest of the sentence is lowercase
- Capitalisation – Where the first letter of every word is uppercase
- Lowercase – No words have capital letters, all are lowercase
- All caps – All letters are capital letters (often used for call-to-action buttons)
The list goes on, but you see the case we’re making (see what we did there?).
We recommend using title case or sentence case. These are the easiest formats for readers and they won’t make your link seem spammy.
Why has Google rewritten my title tag?
From time to time, you might find that a page title looks different to the one you wrote. This can happen due to a few reasons:
- Google thinks it can write a better title – Google makes money by serving up relevant search results. It figures out whether your website is relevant by indexing the content on your page. If Google likes the content but doesn’t think the title tag is very good, it may use a title that’s better optimised to attract visitors.
- Google thinks there’s a more relevant title tag for the search query – Google is likely to rewrite a title tag if it thinks the existing one is irrelevant or generic.
Google has determined your page content based on the anchor text of the inbound link – If your website has been linked from another site using a clickable in-text link, Google might use the anchor text as a title tag when displaying search results.
Can I stop Google from rewriting my title tags?
There’s no way to prevent Google from rewriting title tags. But, you should keep an eye on how Google is displaying your web pages in search results.
As part of your normal SEO work, you should periodically head to Google and search for your own products and services. Take note of how Google is displaying titles that it has rewritten.
Consider incorporating the words, phrases, formatting and grammar that Google has used in your broader title tag strategy. This can boost your rankings and increase the number of visitors to your website.
How to rewrite existing title tags
There are lots of approaches to rewriting existing title tags and optimising them for SEO. Below is just one example of how this can be done effectively:
Step 1 – Run your website through a screening tool such as Screaming Frog. This will show all of your website’s URLs and existing metadata (including page titles, H1s and meta descriptions)
Step 2 – Categorise the data. Export the data from Screaming Frog and keep the following columns:
- URL
- Page Title
- H1
- Meta Description
Step 3 – Using your keyword research, look for opportunities to add your primary keyword and secondary (if applicable) into the title tag. Keep in mind the best-practice approach we discussed above.
Step 4 – Log in to your website and update page titles from the backend of your site.
Step 5 – Use Google Search Console to request re-indexation for each page that had its title tag altered.
Step 6 – If you use a keyword tracking tool (such as Semrush), keep an eye on the keyword positions over the next few weeks to see the outcome of your changes.
Checking your work
We recommend working in a spreadsheet when rewriting title tags. This allows you to write, edit and tweak titles without having to make changes to your live website.
As you go, you can use tools like the ones listed below to simulate how your webpage will be displayed in Google’s search results. Here are some of our favourite Google SERP simulators:
Optimise your title tags for SEO success!
Writing title tags requires time and effort, but it isn’t a complicated task. Nevertheless, title tags will never be perfect, and they shouldn’t be something you set and forget either.
Just keep in mind that the work you do needs to align to your SEO strategy. That means title tags aren’t enough on their own – you also need solid keyword research, well-written content and high quality backlinks to give your title tags the best chance of success.
If you want to get on top of your SEO strategy then the team at Gordon Digital would love to help! We’ve turned title tags into a fine art, so we can optimise your website to attract more leads than ever.
Give us a call to find out more, or book a strategy session to design an SEO strategy that can help kick your business goals!