1. Page Titles / Title Tags
Page titles (also known as title tags) are the most important meta tags when it comes to SEO.
The page title is a short description of the web page. This piece of code appears in the <head> section of your HTML, and it looks like this:
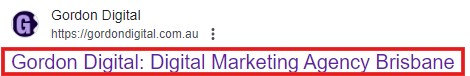
<title>Digital Marketing Agency Brisbane | Gordon Digital</title>While page titles aren’t displayed on the page itself, the tag appears as the clickable link on search engine results pages (SERPs):
Page titles also appear in browser tabs:

The page title is one of the first things users will see when they’re searching for information, so it can heavily impact keyword rankings.
For this reason, it’s important to align the page title to the keyword(s) you are targeting for that specific page. Avoid spamming keywords in the title tag, as it will be looked at unfavourably by Google (and your users!).
For example, let’s say you’re a plumber with a web page that provides details about your drain clearing service. A customer in your local area uses Google to search for a service similar to yours. The search results will likely contain links to plumbing websites, and the page title is the first thing the customers see.
In this case, a good page title would align with your service offering:
Drain Clearing Services
A better page title would align with your service offering and indicate that you’re operating in the user’s local area. This helps satisfy their search intent:
Same-Day Drain Clearing Services in Brisbane
A bad page title would provide inaccurate information about the nature of your web page:
How to Clear a Blocked Drain
If you use a bad page title like this one, a customer might expect to find step-by-step instructions they can try themselves.
This creates a few problems:
- Your web page may not appear when customers search for “drain clearing services” because the keywords in the title don’t match the user’s search intent, making it unlikely for Google to display your page.
- Even if your page was displayed, would a customer who’s searching for a plumber click the link? In this case, it’s unlikely the searcher wants to clear the drain themselves. They’re searching for professional services, and step-by-step instructions may not interest them.
- What happens when someone who’s searching for step-by-step instructions visits your website and discovers that you’re offering a service, rather than advice? They leave your website and continue their search for the information they need.
In all of these cases, using the wrong page title negatively impacts keyword rankings and user experience, and you miss an opportunity to attract a new lead.
Page Title Best Practices
- Use relevant keywords in your page title that match the search intent of the page.
- Keep page titles under 60 characters, otherwise search engines may truncate them in search results.
- Placing your business name at the end of your page title is a common practice, but isn’t a hard rule. Omit your branding if it allows you to better explain the content of the web page.
- Don’t forget to make your page title stand out! Try to balance important keywords with an enticing call to action or unique sell point.
2. Meta Descriptions
The meta description is a short summary of what a web page is about. The meta tag sits in the HTML <head> section and can influence what Google displays in search results.
While meta descriptions aren’t a direct ranking factor, they are crucial in enhancing click-through rates.
A good meta description can entice users to visit your website by including CTAs and promising detailed answers to their queries.
The meta tag looks like this:
<meta name="description" content="Leading digital marketing agency in Brisbane - Gordon Digital. Maximise your brand’s success - generate real, tangible results."/>A web page’s meta description may be displayed under the page title in Google’s search results:

Including keywords that match a user’s search query within your meta description can cause these keywords to be highlighted in bold in the search engine listing. This helps convey what a user will discover when clicking on your page title.
It’s also a good idea to include a strong call to action within your meta description. This helps you stand out amongst other listings and subtly encourages users to visit your website.
Meta Description Best Practices
- Provide each page with a distinct meta description that accurately conveys the page’s value.
- Try to keep your description within a maximum of 150-160 characters (Google may truncate it otherwise, just like page titles).
- Incorporate your most important keywords.
- Avoid keyword stuffing, and make sure you’re using full sentences and correct grammar.
- Try to include an attention grabbing call-to-action or a unique value proposition.
3. Image alt Attributes
The “alt” attribute is a short description that’s embedded within an image tag. It describes what the image shows and is crucial for user accessibility and SEO.
When an image cannot be displayed (e.g. due to loading errors) the alt text is displayed instead. This provides users with a textual description of the missing content and helps to make the page more cohesive.
Alt attributes are also used by people who browse the web with accessibility plugins. These accessibility plugins typically “read out” the content of a web page. Since it’s impossible to read out an image, the plugin will read the alt attribute instead.
Beyond the user, alt attributes are also important for search engines.
Search engines can’t decipher images. Instead, they read the alt attribute to determine what an image is showing. Alt attributes can affect the rankings of web pages, and search engines also use them to rank results in image searches.
Best Practices For Alt Text
- Try to optimise the most significant images (product images, infographics, or instructional images), which are most likely to be searched for in Google Images.
- Include alt text on pages where there isn’t a great deal of content besides the images.
- Ensure the alt text is clear and descriptive – explain what the image shows in basic terms.
- Use keywords if they naturally fit into the description of the alt text.
4. Heading Tags
Heading tags are HTML elements that describe a hierarchy of information. These tags range from H1 to H6, in descending order of importance. These tags are important for differentiating headings and subheadings from other text types, such as paragraph text.
For instance, the H1 heading tag is usually the main title of a web page, while H2 through H6 titles are often used for subheadings within the content.
The significance of heading tags has sparked significant debate within SEO.
First things first: H1 tags are fundamental to your SEO strategy.
Google reads H1 tags in an attempt to understand the core topic of a web page. H2 through H6 tags are less critical, but they help users and search engines categorise your content.
While testing shows that heading tags are important to rankings, Google has consistently communicated that headings do not act as ranking factors.
They have also dismissed the notion of a hierarchy, where H1 tags are viewed as more significant than H2, and so on.
The primary value of heading tags lies in their ability to structure and organise titles for enhanced readability. Moreover, well-structured content is easier for search engines to index, which is a key aspect for optimising search engine visibility.
Heading Tags Best Practices
- Ensure your headings accurately reflect the section of text they describe. Even if they are not a direct ranking factor, search engines still consider their relevance.
- Your headings should capture the essence of the text beneath them. Steer clear of generic titles such as “Chapter 1”.
- Avoid excessive use of keywords within heading tags. Prioritise readability for your users.
5. Robots Meta Tags
The robots meta tag is a piece of HTML that tells search engines how to crawl and index a web page.
Although these tags do not directly influence rankings, they can affect how search engines crawl and interact with your web pages.
Robots tags have several values. A page-level robots meta tag with a “noindex” attribute signals to search engines that a particular page should not be indexed within search results. A “nofollow” attribute indicates that search engines should not follow any links on that page.
The robots meta tag is placed in the <head> section of a web page like so:
<meta name='robots' content='noindex, nofollow'/>
The above example tells search engines to not index the page in search results, and not to follow any links on the page.
While you can technically set a page to NOINDEX while keeping it as FOLLOW, Google has stated that those links will eventually be treated as “nofollow”.
Robots Meta Tag Best Practices
- Use noindex carefully. It prevents search engines from indexing your website. That is, your page won’t appear in search results and users won’t be able to find it through search engines.
- Use the noindex value to prevent search engines from crawling and indexing pages that aren’t useful for ranking, such as duplicate content, or private pages like.
Apply nofollow on external links to avoid passing PageRank or link authority to this linking page. This is helpful for content you’re not sure about, or anything paid (using the ugc and sponsored value is also required).
6. Canonical Tags
A canonical tag is a HTML element that’s used to tell search engines the preferred version of a page.
They’re used when multiple pages on your website have the exact same content (duplicate content) or very similar content that Google is struggling to distinguish between.
In these cases, a canonical tag can point back to the original page that you want indexed for a particular keyword.
Without this, search engines believe you’re showing the same content twice, which can confuse or look manipulative. By providing a canonical tag, search engines are able to better understand which page corresponds to a user’s query.
Note that search engines aren’t compelled to obey canonical tags. If Google decides that one page provides better information than another, it may choose to ignore your canonical tags.
It’s still best practice to avoid having overly similar or duplicate content on two different pages of your website.
Canonical Tags Best Practices
- Use canonical tags to specify the preferred version of a web page where duplicate content exists.
- Ensure the canonical tag is accessible and matches the web page’s URL structure, i.e. www vs non-www URL structure.
7. Meta Viewport Tags
The meta viewport is a HTML tag that tells the browser how to adjust and scale the page relative to the size of the device it’s being viewed from.
This is especially important for smaller devices such as mobiles and tablets.
Without a meta viewport, web pages can be misaligned and appear too small, elements might not fit, or it can create issues with accessibility and readability.
Meta Viewport Tag Best Practices
An ideal meta viewport provides a responsive experience and displays correctly on all devices, especially on mobile devices. The standard code for this is:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
If we break down this code, it tells us the following:
- content=”width=device-width” sets the width of the web page to the width of the screen it’s being displayed on.
- “initial-scale=1” sets zoom level when the page is first loaded by a web browser.
There are other elements to expand on, but this basic format is relevant for the majority of websites.
8. Language Tags
A language tag is a HTML element that advises the primary language used by a web page.
Langage tags are placed within the opening <html> tag. They define the language through standardised ISO codes (also known as ISO 639 Language Codes).
Here’s an example of a language tag for an Australian business:
<html lang="en-AU">This would be slightly different for a US or UK-based business, which would use en-US and en-UK respectively.
Why Are Language Tags Important For SEO?
Language tags are essential for SEO as they help search engines identify the page’s language, ensuring it is delivered to users who speak that language. It also targets content to specific linguistic regions.
Accessibility is the other major reason for language tags. Users who use assistive technologies rely on language tags to properly read and translate the content of a page.
Language Tag Best Practices
- Choose the correct ISO language code to indicate the primary language of the page.
- Ensure content matches the specified language tag.
9. Hreflang Tags
The hreflang tag tells search engines about the language and geographical location of a webpage.
The tag helps search engines to serve the correct language or regional URL, relative to the user’s geographical location and language settings.
This is particularly useful for businesses that operate in multiple languages, multiple regions, or for international websites.
Do I Need Hreflang Tags On My Website?
Hreflang tags are only applicable to websites that serve content to different countries or regions. This can also include ecommerce websites that sell across different international markets.
How Do Hreflang Tags Benefit My Website?
Using hreflang tags properly can benefit your SEO strategy by:
- Preventing your own regional web pages from competing with each other in the search rankings.
- Localising content for all users, improving the user experience.
- Improving the URL structure of international websites.
Hreflang Best Practices
- Use hreflang tags for multilingual or multiregional sites.
- Implement hreflang tags through your website’s HTML or XML sitemap (not both!)
10. Open graph tags
Open Graph tags are part of the Open Graph protocol. They enable web pages to change how content is displayed and shared on social media platforms.
Open Graph platforms are placed in the <head> section of the HTML, They create metadata for social media platforms about the page content that includes:
- Page Title
- Page Type
- Image
- URL
- Sitename
Is Open Graph Useful For SEO?
Open Graph tags do not directly influence search engine rankings. However, social media has been shown to have an indirect increase in web page engagement, and helps with acquiring backlinks to your content. Both of these things can hugely benefit your SEO strategy.
What Does Open Graph Look Like?
Open Graph’s HTML looks like this:
<meta property="og:title" content="The Ultimate Guide to Open Graph Tags" />
<meta property="og:description" content="Learn how to use Open Graph tags to improve your social media sharing and enhance your content's visibility." />
<meta property="og:type" content="article" />
<meta property="og:url" content="https://example.com/open-graph-guide" />
<meta property="og:image" content="https://example.com/images/og-image.jpg" />
<meta property="og:site_name" content="ExampleSite" />Here’s an example of what this code generates when used on a real web page:
This is our homepage. When a link is shared to social media, the Open Graph tag causes the link to be displayed in one of the above ways. This means we get a say in how our branding appears – even on social media platforms.
Open Graph Best Practices
- Optimise Open Graph tags to improve click through and encourage users to share your content by using compelling images and descriptions.
- Ensure your tags are regularly updated.
Grow your SEO strategy with the top 10 essential meta tags
Meta tags are a critical part of your onpage SEO strategy. They improve the way search engines understand and interpret your content, and they’re also important for user experience.
Mastering meta tags is a complex task. There’s lots to learn, and the best way to start is to work with the team at Gordon Digital!
Gordon Digital provides SEO services, including turning meta tags into rankings success. Our experts design strategies featuring onpage optimisations that can help your website get found online.
Start a conversation with us if you’re ready to learn about meta tags and how they fit into your SEO strategy!